What is Work Wear Textile in Medical Sector?
Work wear textile is engineered to protect against contamination of fluids pathogens. In hospitals, barrier textiles prevent the spread of infectious pathogens to both patients and staff. All health care workers must use protective clothing such as gowns, gloves, drapes, facemasks, and caps when in contact with patients to prevent disease transmission. Disposable and reusable textiles are two types of products employed in the healthcare field against infectious pathogens.
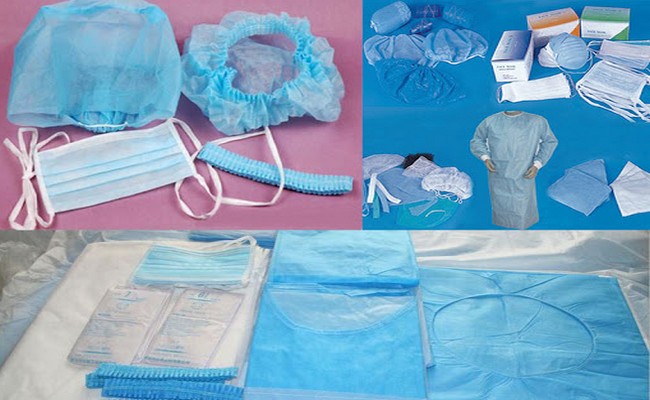
Disposable textile generally serves only as single-use products and then they have to be immediately discarded as bio-hazardous materials. Whereas reusable textiles can be sterilized and laundered for reuse.
Key Characteristics of Medical Workwear Textiles:
1. Antimicrobial Properties:
- Medical textiles often incorporate antimicrobial treatments or fibers to prevent the growth of bacteria and other pathogens. This is crucial in reducing the risk of infections in healthcare settings.
2. Fluid Resistance:
- Medical workwear, such as gowns and scrubs, is often treated to be fluid-resistant or fluid-repellent. This protects healthcare workers from exposure to bodily fluids, blood, and other contaminants.
3. Breathability and Comfort:
- Given the long hours healthcare workers spend in their uniforms, comfort is essential. Medical textiles are designed to be breathable and allow for ease of movement, often incorporating moisture-wicking properties to keep the wearer dry.
4. Durability and Washability:
- Medical workwear must withstand frequent washing and sterilization without degrading in quality. High-quality textiles ensure that the garments remain functional and safe even after multiple uses and cleaning cycles.
5. Barrier Protection:
- For certain procedures, healthcare workers require textiles that offer higher levels of barrier protection against pathogens. This includes gowns, gloves, and masks made from materials like nonwoven fabrics or laminated textiles that provide enhanced protection.
Raw Material Specification and Manufacturing Methods of Work Wear Textile:
Generally, both disposable and reusable medical workwear textiles are made of polymeric fibers, but they have different structures. Disposables are usually nonwoven fabrics, which are produced by closely entangled fibers into a web and then layering the resultant material into sheets.
The fibers used for disposable products are as below:
- Polyethylene,
- Polypropylene,
- Polyester and their blends.
Many disposable textiles also contain wood pulp fibers as a major component. Reusable textiles, which were traditionally made of cotton fibers but it is replaced by polyester due to high durability and low cost.
Nonwoven fabrics for disposable surgical gowns and drapes are made of melt-blown and spun-bond polypropylene and polyethylene fibers which are more advantageous. Whereas for reusable gowns and drapes fabrics are made of spun polyester or cotton fibers woven with high thread density to provide better barrier properties. The facemasks and caps are made of the same material as above in both types but their structures are somewhat less tight than gowns and drapes. All these products are then finished with a microporous film of PTFE to enhance their water repellency and breathability properties to provide better protection along with comfort to the wearer.
Whereas the gloves are made of 100% rubber which does not allow the penetration of infectious fluids through it. These gloves are generally discarded after a single use because it contains high infectious materials after use and reusing them is more hazardous.
Types of Workwear Textiles Used in the Medical Sector:
1. Scrubs:
- Material: Typically made from a blend of polyester and cotton for durability, comfort, and ease of cleaning.
- Usage: Worn by healthcare professionals during routine care and procedures.
2. Lab Coats:
- Material: Usually made from cotton or polyester-cotton blends, sometimes with a fluid-resistant finish.
- Usage: Worn by doctors and laboratory personnel to protect against spills and stains.
3. Isolation Gowns:
- Material: Made from nonwoven fabrics or polyethylene-coated materials that provide a barrier against fluids and pathogens.
- Usage: Used in situations where there is a high risk of contamination, such as during surgeries or handling infectious patients.
4. Surgical Textiles:
- Drapes and Gowns: Surgical textiles include specialized gowns and drapes made from barrier materials that are sterile and provide high levels of protection during surgeries.
- Caps and Masks: These are made from nonwoven or fluid-resistant materials to protect against droplet transmission.
5. Footwear and Gloves:
- Material: Often made from materials like nitrile, latex, or synthetic blends to provide protection and prevent contamination.
- Usage: Gloves protect hands during procedures, while footwear (like disposable shoe covers) prevents the spread of contaminants.